
This phenomenon was first explained by J J Thomson in 1903 and is named after the scientist himself. As it accelerates, it, in turn, emits radiation and thus, the wave is scattered.” It is a very important concept in plasma physics and forms the basis of X-ray crystallography, inverse Compton scattering and the cosmic microwave background.

The electric and magnetic components of the incident wave accelerate the particle.
#JJ THOMSON CATHODE RAY EXPERIMENT SUMMARY FREE#
Thomson Scattering is the “ scattering of electromagnetic radiation by a free non-relativistic charged particle. #6 He was the first to explain Thomson Scattering It is still widely referred today by students and academicians alike. It is a comprehensive text book that aided the understanding of the formation, motion and interaction of vortex rings. The book received acclaim across the scientific community for its explanation of the subject. J.J Thomson’s “Treatise on the Motion of Vortex Rings” is a seminal text on the subject and it won the Adam’s Prize in 1882.

#5 His Treatise on the Motion of Vortex Rings is a seminal text on the subject A Treatise on the Motion of Vortex Rings by JJ ThomsonĪ vortex is a region where a fluid or gas spins around an imaginary axis that forms a closed loop.

This was the first instance of different isotopes being discovered in a stable element. They discovered two different patches of light, which led them to conclude that neon was made up of particles with different atomic masses, or isotopes. They channel l ed neon ions through a magnetic and an electric field on to a photographic plate. Aston conducted experiments on streams of positively charged particles. In 1912, Thomson and his research assist F.W. Earlier it was widely believed that stable or non-radioactive elements did not have isotopes. Isotopes are variants of a chemical element that have different numbers of neutrons. #4 He discovered the first evidence of different isotopes in a stable element This laid the groundwork for the development of cathode ray tubes which could be used to modulate, accelerate and deflect electron beams onto a screen to create images, thus leading to the invention of the first television sets. This proved that the electrical charge was inseparable from the ray itself. During his cathode ray experiments, Thomson applied a magnetic field across the cathode ray tube, thus discovering that the rays were bent away by the magnetic field. Earlier, scientists were not sure whether the electric charge from the cathode ray could be separated from the ray itself. The Cathode Ray formed the fulcrum of many modern day inventions such as the very first televisions. #3 His cathode ray experiments aided the invention of the first televisions Thomson’s discovery completely overturned the prevalent belief that atoms were the ‘building blocks of life’ and the smallest particles in the universe. Later these particles would be named electrons.
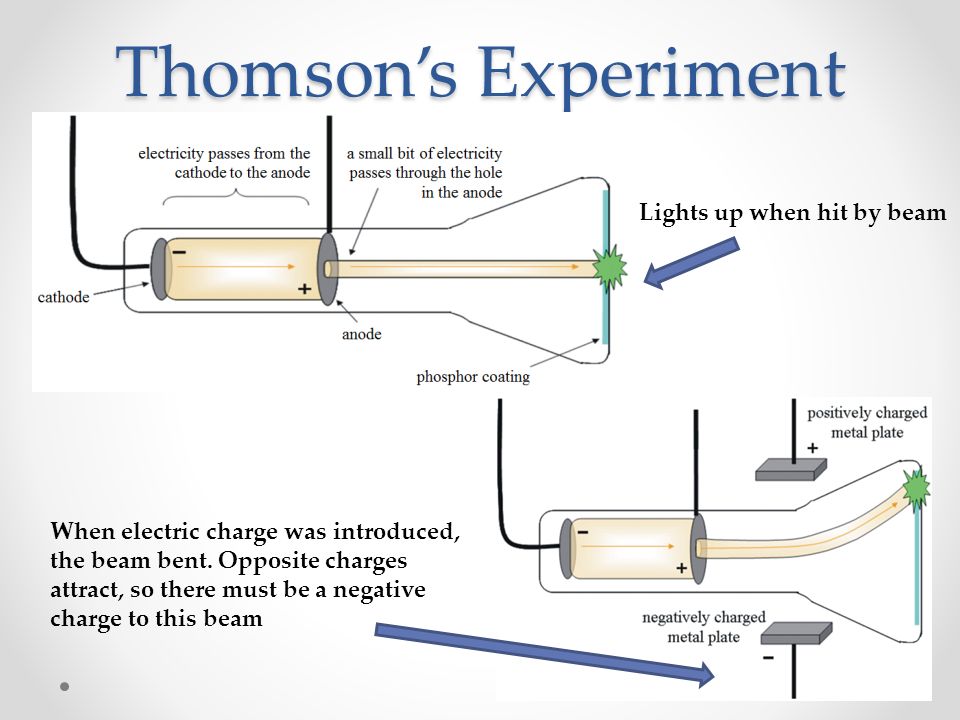
In May, 1987 he announced the first discovery of sub-atomic particles, which Thomson would call ‘corpuscles’. Thomson thus discovered particles that were 1,800 times lighter than the lightest atom (hydrogen). Thomson conclusively proved otherwise through his experiments with cathode ray tubes that showed that all atoms contain tiny negatively charged subatomic particles. In 1906, Thomson was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics “in recognition of the great merits of his theoretical and experimental investigations on the conduction of electricity by gases.” #2 Sir J J Thomson discovered the electronįrom the late 17th century onward, it was widely accepted among the scientific community that the atom was the smallest unit of matter. This research was widely recognized as one of the most important work being done in the scientific community at the time. In 1897, Thomson showed that cathode rays consisted of particles, electrons, that conduct electricity. #1 He did groundbreaking work in conduction of electricity in gases Conduction Of Electricity Through Gases by JJ ThomsonĬ athode rays are radiation emitted when a voltage is applied between two metal plates inside a glass tube filled with low-pressure gas.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
